DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment
DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment Details:
In this assignment, learners are required to write a case report addressing the personal knowledge and skills gained in the current course and potentially solving an identified practice problem.
DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment General Guidelines:
Use the following information to ensure successful completion of the assignment:
This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
Doctoral learners are required to use APA style for their writing assignments. The APA Style Guide is located in the Student Success Center.
This assignment requires that at least two additional scholarly research sources related to this topic, and at least one in-text citation from each source be included.
You are required to submit this assignment to Turnitin. Please refer to the directions in the Student Success Center.
DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment Directions:
For a specific focus of patient practice (e.g., acute care hospital, clinic, primary care, long-term care, home health), select a particular disease process DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment. Identify and fully describe the required technology elements that will be involved in providing care and define how these technologies will integrate treatment and/or monitoring from the identified care setting to the home and then to ongoing care.
Your case report must include the following:
Introduction with a problem statement
Brief literature review
Description of the case/situation/conditions
Discussion that includes a detailed explanation of the synthesized literature findings
Summary of the case
Proposed solutions
Conclusion
Portfolio Practice Hours:
It may be possible to earn Portfolio Practice hours for this case report. Enter the following after the references section of your paper:
SAMPLE SOLUTION APPROACH TO THE CASE REPORT
Case Report: Health Care Informatics
DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment Introduction
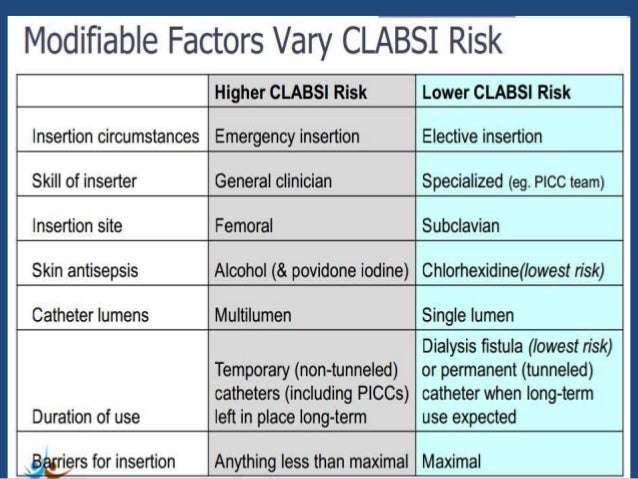
Central line associated blood stream infections (CLABSIs) continue to be a huge expense for health care organizations across the US as they cause harm to patients. Some studies have estimated that the cost of a single CLASI episode can be as much as $25,000.
Therefore, a reduction in the use of central lines in hospitalized patients can help to reduce the number of days that patients have the catheters in place and also reduce the number of CLABSIs a patient may encounter (Pathak, Gangina, Jairam & Hinton, 2018). Studies have shown that the use of care bundles that include the removal of catheters that are no longer needed is one of the most effective ways of preventing CLABSIs (Atkilla, Doganay, Celik, Tomak, Gunal, & Kilic, 2016).
However, when a central line is essential to the care of the patient, implementing measures to prevent CLABSIs is essential to prevent infections. The problem is that in the inpatient setting, nurses forget to give patients with central lines chlorhexidine baths daily as indicated per hospital protocol or they forget to documentation DNP 805 Week 7 Case Rport Health Care Informatics Assignment.
They may also forget to do the documentation of the bath even when it has been completed and leaves nurse leaders with gaps in the medical record to understand what happened when CLABSIs do occur. In this paper, the author will discuss the literature review that supports the use of chlorhexidine baths to prevent CLABSIs, discuss a case study of a patient who developed a CLABSI and describe the type of technology that is needed to help nurses take better care of patients who have a central line in place in order to prevent CLABSIs.
Applicable Care Based Technologies
Several care based technologies are possible solutions to help prevent CLABSI’s. An electronic health record (EHR) can be used to provide clinical decision prompts to allow for timely care for patients (Alexander, S., Frith, K.H., & Hoy, 2019). Computer physician order entry (CPOE) can prompt a reflex order that is generated to complete daily chlorhexidine baths whenever a physician documents or enters treatment with the insertion of a central line on a patient.
Additionally, the EHR can be designed to prompt nurses to provide chlorhexidine baths as a daily intervention that requires documentation to be completed. Clinical decision support (CDS) can be implemented in the EHR to provide alerts and reminders for patient care, provide focused data reports and summaries and provide documentation templates to help with patient care compliance (Alexander, S., Frith, K.H., & Hoy, 2019).
Integration of Technologies and Treatment/Monitoring in Care Settings
The implementation of an EHR has many possibilities for leaders in different healthcare settings that include inpatient and outpatient settings, and doctor’s offices. Records are easily accessed, data entry can be simplified, and multiple practitioners can access the records at the same time DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment.
Care can be collaborated faster and easier with an EHR than with the old paper record system and the integration of decision support technology can quickly bring the most up to date evidence based practice to the practitioner at the point of care.
Treatment and follow up can happen quickly due to the ease and accessibility of (Alexander, S., Frith, K.H., & Hoy, 2019). Therefore, with the implementation of technologies that are integrated in the EHR, a feasible solution can be found to help nurses to remember to complete chlorhexidine baths in the intensive care unit or for patients in an inpatient setting who have a central line in place.
Literature Review
In identifying a technological solution to the problem related to nurses not being compliant or consistent in giving chlorhexidine baths to prevent CLABSIs, a total of four articles were reviewed related to the use of chlorhexidine bed-baths to reduce central line associated blood stream infections (CLABSIs).
Sarani, Navidian, Jahani, Tabas & Bidar, (2017) completed a quasi-experimental study with 80 patients admitted to an ICU in a teaching hospital. Patients in the inclusion group were bathed daily with chlorhexidine 2% solution. The patients in the control group did not get a daily bath with the chlorhexidine solution.
The study revealed that 100% of the control subjects had positive culture growth after 5 days of being in the ICU without having a chlorhexidine 2% bath and identified the effectiveness of the 2% chlorhexidine solution in preventing skin colonization and skin infections in ICU patients. In a second study, Cleves, Pino, Patino, Rosso, Velez & Perez (2018) demonstrated a significant reduction in CLABSI rates in neonates with the use of chlorhexidine baths.
A reduction from 8.64 to 4.28 was seen CLABSIs per 1000 was observed in the unit. A third study by Reagan et al., (2019), showed that an increase in chlorhexidine bathing compliance from 60% to 90% prevented 20 infections and saved almost one million dollars in costs for patient care DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment.
As bathing compliance increased, the study showed that the overall costs of infections subsequently decreased. Kim, Lee, Na, Roh, Shin & Kim (2016) completed a meta-analysis with eighteen studies that concluded that there was a greater reduction for CLASISs among critically ill patients with chlorhexidine bathing. The study found that the risk for CLABIs is reduced when chlorhexidine baths are completed daily.
Description of Case
On day 1, Patient Clark (PC), a 67 year old female, was admitted to the cardiovascular intensive care unit (ICU) with an acute myocardial infarction. On day 2, a central line was placed and she was taken to the cardiac catheterization lab. On day 4, the central line was still in place.
PC became confused and she was having chills and her temperature was 38.4 degrees Celsius. She went from a sinus rhythm on the cardiac monitor to a sinus tachycardia and her blood pressure dropped from 120 systolic to 92 systolic. An infection was suspected and the physician ordered blood cultures to be drawn. On day 5, the culture was resulted and identified enterococcus faecalis as the organism in the blood. Since the central line was in place for greater than 2 calendar days on the date of the fever and there was no other identified site of infection, PC was diagnosed with a central line associated bloodstream infection. DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment
A review of the chart indicated that the nurses had not documented a chlorhexidine bath on days 2, 3 or 4 of her stay in the intensive care unit. Although a daily chlorhexidine bath was a unit based protocol for infection prevention in the critical care unit, the nurses had not consistently ensured or documented that she had received the bath. The infection control nurse and nurse educator of the intensive care unit reviewed potential root causes of the CLABSI and identified the lack of completion of daily chlorhexidine baths as contributing to the CLABSI. DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment